Quarter Coin: History, Value, & Hidden Worth Revealed – 2025

Understanding the “Quarter Coin” Concept
When you hear quarter coin, what springs to mind? For many of us in the United States, the image of a 25-cent piece—one-quarter of a dollar—instantly appears. Yet the term can carry more layers: historical significance, collector interest, design evolution, even metaphorical uses in finance or culture. In this article we explore quarter coin in all its dimensions: what it is, why it matters, how it’s evolved, and how you might think about it today.
Table of Contents
What Is a Quarter Coin?
Basic Definition
A quarter coin is a coin whose face value equals one-quarter of the base currency unit (for example, one-quarter of a dollar). In the U.S., a quarter (officially a “quarter-dollar”) is worth 25 cents, or 0.25 USD. (Wikipedia)
Why the Name “Quarter”?
The term “quarter” simply indicates one fourth. In currency terms, it means break the unit into four parts, and the quarter coin represents one of those parts. This is a handy size both in commerce and in everyday conversation (“two bits”, “give me a quarter”, etc.).
Composition & Minting
Over the years the U.S. quarter coin has changed in composition. From 1932 to 1964, it was 90% silver and 10% copper. Afterward, the composition shifted to cupronickel clad over copper. (Wikipedia) These changes reflect rising material costs, manufacturing methods, and evolving minting priorities.
A Brief History of the Quarter Coin
Early Origins
The U.S. quarter dates back to 1796 and has had continuous production since 1831. (Wikipedia) Early designs varied—Draped Bust, Capped Bust, etc.—each telling its own historical and aesthetic story.
The Washington Quarter and Beyond
In 1932, the iconic Washington quarter was introduced, featuring George Washington on its obverse side. (Wikipedia) Over time, reverse designs have changed frequently—state quarters, America the Beautiful series, commemoratives—offering collectors plenty of variety. (Wikipedia)
Modern Era and Collector Appeal
While today most quarters circulate as everyday currency, many collectors focus on earlier silver ones (pre-1965), special mint marks, rare errors, or limited-edition issues. Their value often exceeds face value depending on condition, rarity, and demand.
Why the Quarter Coin Matters
In Everyday Transactions
For average people, the quarter coin plays a practical role—making change, vending machines, parking meters, small purchases. It’s a workhorse coin in everyday commerce.
In Numismatics (Coin Collecting)
For collectors, the quarter coin is a beloved entry-point. Because of its variety and long history, one can collect quarters from different eras, designs, mints, and conditions. Some high-grade or rare pieces command significant premiums.
In Cultural and Historical Context
The quarter coin reflects design trends, technological changes in minting, economic realities (like metal cost shifts), and even national imagery. For example, the 50-State quarter program (1999-2008) intentionally tied money to regional pride and U.S. heritage.
As a Metaphor
Beyond its literal form, “quarter coin” (or just “quarter”) can symbolize small increments, fractional value, or partial ownership: getting a quarter share, giving someone a quarter, or splitting things into quarters. It’s embedded in everyday language.
Anatomy of a Quarter Coin
Obverse (Front) Features
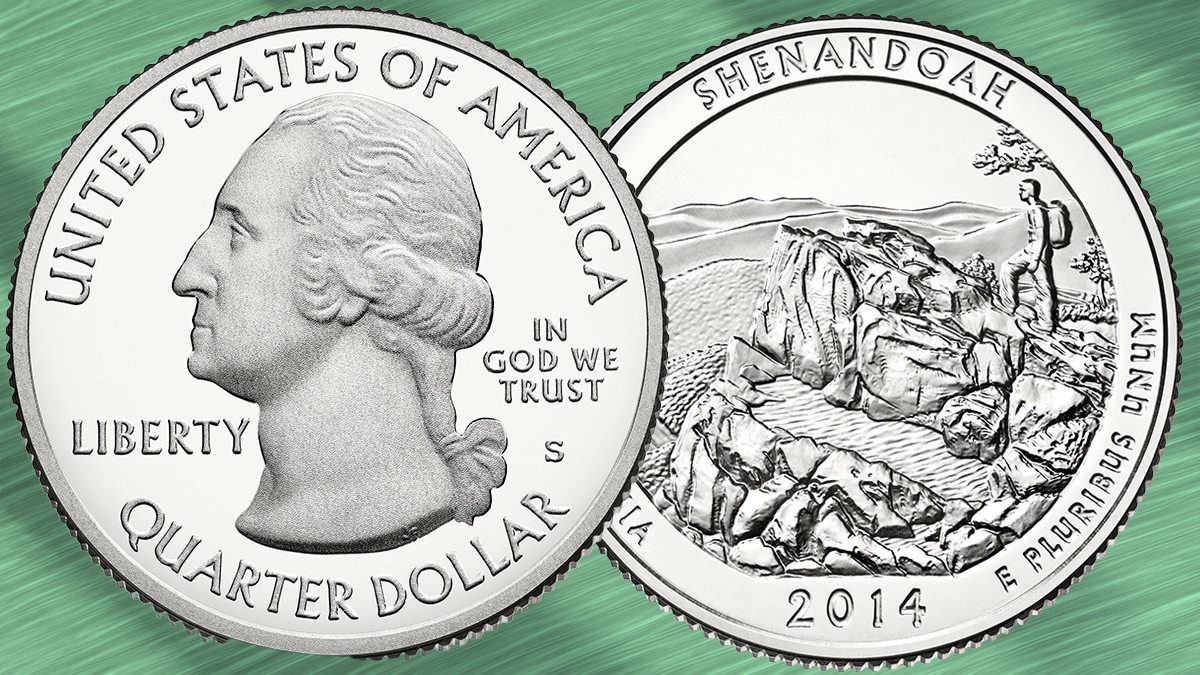
Typically, the obverse of a U.S. quarter shows a national figure (e.g., George Washington since 1932) along with inscriptions like the year, mint mark, “Liberty”, and “In God We Trust”. (Wikipedia)
Reverse (Back) Features
The reverse has varied enormously: from an eagle to state-specific imagery, to national parks in the America the Beautiful series. These changing designs add visual appeal and collectible interest. (Wikipedia)
Edge, Diameter, and Composition
A modern U.S. quarter has a diameter of about 24.26 mm (0.955 inches) and 119 reeds (grooves) along its edge. Composition since 1965: clad copper (91.67% Cu, 8.33% Ni). (Wikipedia) Earlier silver ones weighed more and contained 90% silver. The physical specs matter to weight, metal value, and authenticity.
Collecting Quarter Coins — Getting Started
Why Collect Quarters?
They’re affordable entry coins with broad variety.
Long history means many designs and mint marks.
Some pieces have rarity or unique features making them significantly valuable.
It’s fun: you can build sets (state quarters, years, mint marks) and enjoy the hunt.
Key Factors to Consider
When evaluating a quarter coin, keep in mind:
Date & Mint Mark: Different mints (P, D, S, W) and years have different rarities.
Condition (Grade): Wear, luster, marks matter. “Uncirculated” coins command more.
Composition/Metal Content: Silver quarters (pre-1965) have intrinsic metal value.
Design & Variation: Limited-edition designs, special mintages, errors.
Provenance & Certification: Certified coins (e.g., by PCGS or NGC) often yield better trust and value.
Popular Quarter Coin Sets and Themes
Washington quarters (1932-present)
State quarters program (1999-2008)
America the Beautiful quarters (2010-2021)
Commemorative quarters & special issues
Each of these offers a clear “theme” for a collector to follow.
Value of a Quarter Coin — Face vs. Real Value
Face Value
At its simplest, a quarter coin is worth $0.25 in circulation. But value is rarely that simple in the world of coins.
Metal Value
For pre-1965 U.S. quarters, the silver content alone often makes the coin worth more than face value. Modern clad quarters have far less intrinsic metal value.
Numismatic Value
A quarter coin’s collectible value depends heavily on rarity, condition, demand, and historical significance. A well-preserved error piece could fetch hundreds or thousands of dollars, even if similar pieces are common.
Real-World Example
Consider an older quarter from 1932 in excellent condition with an “S” mint mark. Its value might be many times $0.25 simply because it’s rare and sought-after by collectors. In contrast, a standard 2015 clad quarter has little premium beyond face value unless it has an error or spectacular condition.
The Quarter Coin in Today’s Economy
Circulation and Usage
In everyday commerce, quarter coins remain relevant: parking meters, vending machines, tip jars, coin-only machines. They maintain ease of use and standardization.
The Impact of Digital Payments
With rising digital payments and contactless transactions, physical coins may see reduced use. Still, coins remain a tangible part of our monetary experience and cultural heritage.
Inflation and Metal Costs
As metal costs (nickel, copper) rise and inflation erodes purchasing power, questions arise: How long will coin production remain cost-effective? Should face values adjust? Some countries have even “phased out” smaller denominations due to cost. Thus, the quarter coin remains under economic scrutiny.
Collectibles Market Outlook
For collectors, the interest in quarters is steady. Special issues (state quarters, America the Beautiful) still spark enthusiasm. Condition quality is key, especially as “good” condition coins become scarcer in circulation.
Quarter Coin Design Highlights
State Quarters Program (1999-2008)
This program introduced unique reverse designs for each U.S. state, boosting public interest and collector engagement. It turned a mundane coin into a collectible story piece.
America the Beautiful Quarters (2010-2021)
These showcased national parks and historic sites, combining numismatic interest with national pride. (Wikipedia)
Error Coins & Special Mintages
Errors (double die, off-center strikes, missing mint marks) and special limited runs can dramatically increase a quarter coin’s value. Collectors often search for these “hidden gems”.
Aesthetic & Historical Symbolism
Each design reflects aesthetic values of its time. The evolution of the quarter coin mirrors U.S. history: the changing portrait of Liberty, the shift from silver to clad, the introduction of thematic designs. It’s a small piece of history in your pocket.
Common Myths and Misconceptions
“All quarters are only worth 25 cents.”
False. While many are only worth their face value, some quarters—especially rare, old, or silver ones—are worth far more.
“Only pre-1965 quarters matter.”
While it’s true that pre-1965 silver quarters often have higher value, modern quarters can also have collectible value—depending on design, rarity, and condition.
“Condition doesn’t matter much for common quarters.”
Condition matters a lot. Even common dates in “mint state” (no wear) can earn a premium. A circulated coin may sell at or slightly above face value, while an uncirculated version could sell for much more.
“Quarter coins are obsolete.”
No — they remain widely used in circulation, still relevant for commerce, and still a favorite among many collectors.
How to Identify a Valuable Quarter Coin
Date & Mint Mark Check
Look for the year and a mint mark (P, D, S, W). Certain years/mint marks have low mintage or higher demand → higher value.
Condition Grading
Use standard coin grading terms: Good (G), Very Good (VG), Fine (F), Very Fine (VF), Extremely Fine (EF), About Uncirculated (AU), Uncirculated (MS). The higher the grade, the more value (generally).
Composition & Weight
For U.S. quarters pre-1965, silver content adds value. Check weight and metal composition if in doubt.
Rarity & Demand
Reference coin catalogs or price guides. If a quarter coin has a rare error or unusual design, it may command a premium.
Authentication & Certification
For high-value coins consider slabs/certification from trusted agencies (e.g., PCGS, NGC). This gives buyers confidence and often improves resale value.
How to Care for Your Quarter Coin Collection
Storage Tips
Use acid-free coin holders, flips, or capsules.
Store in a cool, low-humidity environment.
Handle by the edges; avoid fingerprints or oils.
Keep older silver coins separated from clad coins (to avoid chemical interactions).
Cleaning Warning
Avoid cleaning coins—especially collectible ones. Cleaning can reduce value drastically. Let natural patina and wear remain.
Regular Inspection
Check your collection periodically for signs of tarnish, damage, or environmental issues.
Documentation & Cataloging
Keep a list of your coins: year, mint mark, condition, purchase price, and provenance. This helps track value over time and can be helpful for insurance or eventual sale.
Selling or Trading Quarter Coins
Know the Market
Research current values using coin catalogs, online marketplaces, auction results. The value of quarter coins can fluctuate based on metal prices, collector demand, and rarity.
Choose the Right Venue
You might sell to: local coin shops, online platforms, auctions, coin shows. Each has pros/cons in terms of convenience, fees, reach, and price.
Price Realistically
Avoid expecting “jackpot” prices unless you truly possess a very rare specimen. Many quarters are plentiful and sell near face value plus a modest premium.
Prepare for Authentication
If you’re selling high-value coins, certification and proper documentation improve buyer confidence and can enhance value.
Quarter Coin as an Investment?
Limited Investment Value
While some rare quarters may offer appreciation, in general coins should be treated more as collectibles or hobbies than primary investments. The value may not grow predictably or significantly compared to stocks or other assets.
Diversify Expectations
If you choose to invest, do so within a broader portfolio, and focus on quality (rare date, good condition) rather than quantity of common pieces.
Understand Market Risks
Changes in metal prices, collector interest, and broader economic factors can all impact coin value. There are holding costs (storage, insurance) and liquidity limitations.
Enjoyment Returns Matter
Beyond financial returns, the enjoyment of collecting, the historical connection, and the aesthetic pleasure are often the best “returns” for many collectors.
Quarter Coin in Global Context
Quarters Beyond the U.S.
Many countries have coins worth one-quarter of their base unit (¼ unit). Though we focus on the U.S. quarter coin, similar concepts exist elsewhere: quarter of a pound, quarter of a currency unit, etc.
Comparative Value & Purchasing Power
A quarter coin’s purchasing power changes over time. What you could buy with $0.25 decades ago is different today. This shift shows how coins reflect broader economic change.
Cross-Cultural Collecting
Some collectors specialize in “quarters” or quarter-units worldwide—looking at design evolution, minting practices, and historical context globally.
The Future of the Quarter Coin
Continued Circulation vs. Digital Shift
Physical coins likely remain for now, but as digital payments accelerate, the role and production of quarter coins may evolve. Will there be fewer coins minted? Will denominations change? These are open questions.
Collectible Market Trends
Collectible interest may continue growing for high-quality, rare quarter coins, especially as older coins are increasingly removed from circulation or lost. Condition and rarity will matter more.
Environmental and Production Pressures
Coin production involves metal, energy, and logistics. If costs rise, mints might reduce production or change materials/designs. This could affect future quarters’ scarcity and value.
The Legacy of the Quarter Coin
Whatever happens, the quarter coin remains a symbol of currency design, everyday commerce, national identity, and collecting passion. It’s more than just 25 cents—it’s history, culture, and craftsmanship in your pocket.
Summary of Key Takeaways
Definition: A quarter coin is typically one-fourth of a currency unit (e.g., 25c USD).
History & Design: The U.S. quarter coin has a rich design history from 1796 to present, with various series and compositions.
Value Factors: Date, mint mark, condition, composition, rarity and demand all influence value beyond face value.
Usage: Still relevant in everyday commerce and especially for collectors.
Collecting Tips: Focus on quality, storage, documentation, and realistic expectations.
Investment Perspective: Manage expectations—treat quarters as collectibles, not guaranteed wealth builders.
Future Outlook: Digital payments, production costs, collector scarcity, and material shifts will influence the quarter coin’s evolution.
Why We Should Care About the Quarter Coin
Because the quarter coin is a simple object loaded with narrative. It touches commerce, culture, craftsmanship, and collecting. Every time you hold one, you hold a fragment of history. Whether you’re dropping it into a parking meter or filing it carefully into a coin album—this tiny metal circle carries stories. It reminds us that even common objects can carry extraordinary value—monetary, aesthetic, historical, and emotional.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the quarter coin is far more than just a 25-cent piece. It’s a window into history, economics, design, and human behaviour. From its origins and evolving composition to its place in commerce and collecting, the quarter coin invites us to pay attention—to small things that carry big meaning. So next time you pull one out of your pocket, think: you’re holding a slice of currency, a quarter-slice of a story, and perhaps a whisper of the past. Happy collecting!
FAQs
Q1: Are all quarter coins worth only 25 cents?
A1: No. While many quarters circulate at face value, some—with rare dates, mint marks, errors, or in excellent condition—can be worth much more.
Q2: How can I tell if my quarter coin is valuable?
A2: Check the date, mint mark, condition (grade), composition (silver vs. clad), and see if it’s part of a rare design or error. Certification helps for higher-value pieces.
Q3: Should I clean my old quarter coins to increase value?
A3: No. Cleaning often damages the coin’s patina or surface and can reduce its collectible value significantly. Handle with care instead.
Q4: Is collecting quarter coins a good investment?
A4: Collecting can be rewarding but should be done with realistic expectations. Some coins appreciate, many don’t significantly. Treat it as a hobby with potential value, not guaranteed return.
Q5: Will quarter coins become obsolete because of digital payments?
A5: Possibly their usage in everyday small transactions may decline, but physical coins still hold cultural and collectible value. Production, design and usage may evolve, but quarters are unlikely to vanish overnight.
for more visit The Brypto Bit